Economy
S.Korean growth outlook dims on increased trade deficit
Chip exports have declined since August 2022, worsening the negative trade balance; government revenue has shrunk due to less tax
By May 11, 2023 (Gmt+09:00)
2
Min read
Most Read
LG Chem to sell water filter business to Glenwood PE for $692 million


Kyobo Life poised to buy Japan’s SBI Group-owned savings bank


KT&G eyes overseas M&A after rejecting activist fund's offer


StockX in merger talks with Naver’s online reseller Kream


Mirae Asset to be named Korea Post’s core real estate fund operator



South Korea’s exports are on course to drop for the eighth consecutive month as they declined in the first 10 days of May, data showed on Thursday, further darkening the outlook for Asia’s fourth-largest economy.
The state-run Korea Development Institute (KDI) also slashed its growth outlook for this year to 1.5% from the previous 1.8%, given sluggish overseas sales of semiconductors, the trade-dependent country’s top export item.
The country’s exports from May 1 to 10 reached $14.5 billion, down 10.1% from the same period last year, according to Korea Customs Service. It is the first time since December 2018-January 2020 that Korea’s exports have fallen for more than seven months in a row.
The country’s cumulative trade deficit this year reached nearly $30 billion, 60% more than the deficit last year.
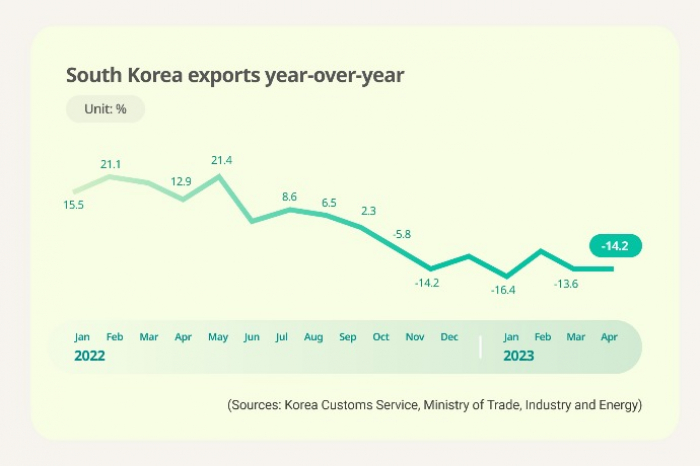
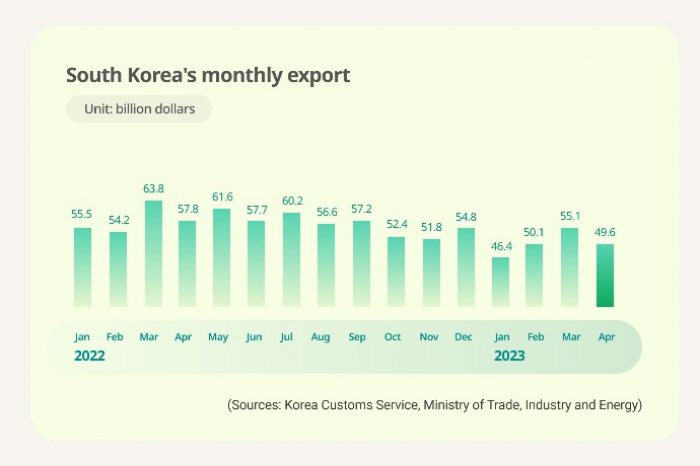
FALLING SALES OF MAJOR ITEMS
For the first 10 days of May, semiconductor exports showed a 29.4% drop on-year. Chip exports declined for nine consecutive months until last month.
Exports of ships, petroleum products and precision equipment respectively declined 49.3%, 40.1% and 10.1% for the first 10 days of this month, compared with the same period last year. Car and auto part exports rose 125.8% and 7.8%, respectively.
Korea’s exports to China, the largest trading partner, have dropped since June of last year. For the first 10 days of May, exports to China, Taiwan, Vietnam and Japan declined 14.7%, 56.5%, 9% and 4.5%, respectively, from a year ago. Conversely, exports to the US and European Union respectively increased by 8.9% and 11.5% during the same period.
Korea imported $18.7 billion for the first 10 days of this month, down 5.7% on-year. Crude oil and semiconductor imports fell 17.3% and 6.1%, respectively; gas and machinery rose 23.5% and 35.1%, respectively.
DIMMER ECONOMIC GROWTH OUTLOOK
The government is also struggling with a negative balance.
Korea’s cumulative revenue in the first quarter of this year was 145.4 trillion won ($109.5 billion), down 14.7% from the same period of 2022 due to slashed income and corporate taxes amid the economic downturn.
Its fiscal balance, which deducts expenditures and pension contributions from total revenue, marked negative 54 trillion won as of end-April. It is already close to the government forecast of a 58.2 trillion won deficit for the entire year.
State-run research institute KDI cut the country’s growth outlook by 0.3 percentage points to 1.5% on Thursday due to the slow recovery of semiconductor exports. The figure may further drop to the low 1% range if demand for chips remains sluggish, it said.
The country’s annual exports will fall 7.6% this year, KDI noted.
Meanwhile, Korea’s private consumption is expected to see a strong recovery, particularly in travel and services. KDI predicted consumer expenditure growth for the year at 3%, up 0.2 percentage points from the previous forecast in February.
Write to Kyung-Min Kang, Sang-Yong Park and Se-Min Huh at kkm1026@hankyung.com
Jihyun Kim edited this article.
More to Read
-
 EconomyS.Korea logs biggest-ever current account deficit in Jan on export slump
EconomyS.Korea logs biggest-ever current account deficit in Jan on export slumpMar 10, 2023 (Gmt+09:00)
2 Min read -
 EconomyS.Korea’s exports drop for 5th straight month in Feb on plunging chip sales
EconomyS.Korea’s exports drop for 5th straight month in Feb on plunging chip salesMar 02, 2023 (Gmt+09:00)
5 Min read -
 EconomyS.Korea’s trade outlook dismal in Feb with stagnant exports
EconomyS.Korea’s trade outlook dismal in Feb with stagnant exportsFeb 13, 2023 (Gmt+09:00)
2 Min read -

Comment 0
LOG IN


