Future mobility
Hyundai Motor expands partnership with quantum computing firm IonQ
IonQ co-founder advises startups to seek out opportunities to serve quantum computers' end users
By Apr 20, 2022 (Gmt+09:00)
3
Min read
Most Read
LG Chem to sell water filter business to Glenwood PE for $692 million


Kyobo Life poised to buy Japan’s SBI Group-owned savings bank


KT&G eyes overseas M&A after rejecting activist fund's offer


StockX in merger talks with Naver’s online reseller Kream


Mirae Asset to be named Korea Post’s core real estate fund operator



IonQ and Hyundai Motor Co. announced a new project on Wednesday designed to apply quantum machine learning to image classification and 3D object detection for future mobility.
The latest agreement between the Maryland-based quantum computing firm and the South Korean automotive behemoth is an expansion of their existing partnership.
FUTURE OF MOBILITY
Experts expect Hyundai’s computational functionality to improve significantly with the incorporation of IonQ’s techniques.
Using breakthrough technology in encoding images into quantum states, IonQ is already well underway in classifying 43 types of road signs using its own quantum processors. The next phase will see the two companies apply IonQ’s machine learning data to Hyundai’s test environment and simulate various real-world scenarios.
President and CEO of IonQ Peter Chapman said: “From partnering on battery research for electric vehicles to image classification and object detection research for automated driving, we expect to see quantum computers become an even more integral part in developing novel transportation solutions.”
IonQ and Hyundai will look to expand current work on recognizing road signs to include other objects like pedestrians or cyclists.
The leader in quantum computing claims its latest quantum computer Aria will enable more efficient processing of object recognition tasks at a lower cost. With 20 algorithmic qubits, IonQ Aria is thought to be the industry’s most powerful such computer based on standard application-oriented industry benchmarks.
Back in January, the two companies announced their decision to use quantum computers in improving the performance, cost and safety of lithium batteries for electric vehicles.
IonQ was founded in 2015 by Kim Jungsang and Chris Monroe after more than 25 years of research. The co-founder and CTO Kim said there were fewer than 10 quantum computing startups when the company was founded. As of last year, there are more than 200 startups in the sector worldwide.
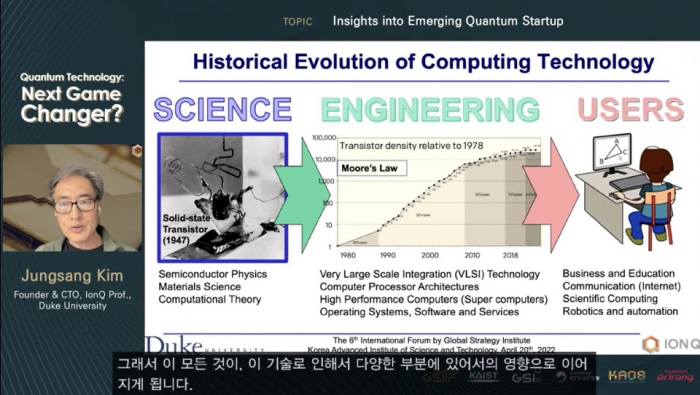
Kim was speaking at Wednesday’s conference Quantum Technology: The Next Game Changer hosted by the Global Strategy Institute of Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST).
So why should we care what quantum computing is and how it differs from traditional computers?
“Quantum physics is the fundamental theory of how matter behaves at a microscopic level and that has been the basis of important technological developments in the 20th century,” Director of the Institute for Quantum Information and Matter at California Institute of Technology John Priskill said during his keynote speech at the KAIST conference.
But the theoretical physicist explained that those technologies don’t scratch the surface of how quantum technology has changed the world we live in.
IonQ’s Kim Jungsang echoed this sentiment.
The renowned academic stressed quantum computing has moved on from a purely scientific research arena and now is making its way into the engineering domain. “When the technology becomes real, it reaches billions of people who don’t care very much about the science behind it,” he said.
The Duke University professor explained what they will care about is getting useful quantum computers and this is where startups should look for business opportunities. The key to success in the quantum computing industry is to “make it accessible to many people and allow people to innovate,” Kim said.
In 2019, Samsung and Mubadala led the next round of funds, which resulted in $55 million. The company also announced partnerships with US tech giants Microsoft and Amazon Web Services to make quantum computers available via the cloud.
Over the course of 2020 and 2021, IonQ built additional generations of quantum hardware and added Google Cloud Marketplace to its cloud partner roster.
On Oct. 1, 2021, the startup became a public company, trading as IONQ on the New York Stock Exchange.
Write to Jee Abbey Lee at jal@hankyung.com
More to Read
-
 AutomobilesHyundai Motor launches robotaxi service in upscale Gangnam district
AutomobilesHyundai Motor launches robotaxi service in upscale Gangnam districtFeb 09, 2022 (Gmt+09:00)
4 Min read -

-
 Corporate restructuringHyundai Motor reshuffles overseas units to deal with changing markets
Corporate restructuringHyundai Motor reshuffles overseas units to deal with changing marketsDec 19, 2021 (Gmt+09:00)
3 Min read
Comment 0
LOG IN


