Green Cross in talks with Russia to produce COVID-19 vaccine
By Mar 18, 2021 (Gmt+09:00)
LG Chem to sell water filter business to Glenwood PE for $692 million


Kyobo Life poised to buy Japan’s SBI Group-owned savings bank


KT&G eyes overseas M&A after rejecting activist fund's offer


StockX in merger talks with Naver’s online reseller Kream


Mirae Asset to be named Korea Post’s core real estate fund operator
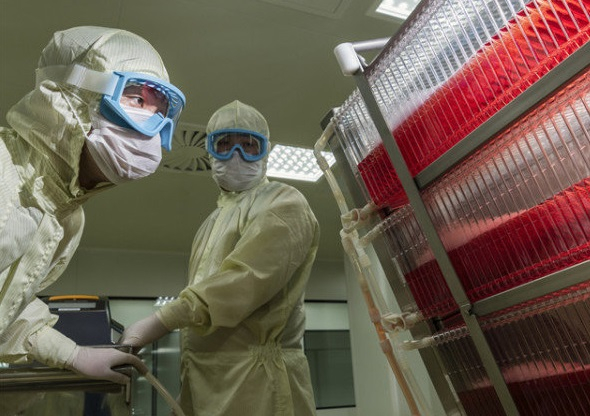



South Korea’s pharmaceutical company Green Cross Corporation (GC) is holding a series of close meetings on contract manufacturing of Russia’s COVID-19 vaccine CoviVac, according to industry sources on Mar. 17.
CoviVac, developed by Chumakov Federal Scientific Center for Research and Development of Immune and Biological Products, is Russia’s third vaccine after Sputnik V and EpiVacCorona.
Chumakov Center representatives and Russian health officials will arrive in South Korea on Mar. 20 to inspect GC’s vaccine manufacturing facilities from Mar. 23.
The chief executive of Russia’s Smart Biotech, responsible for CoviVac’s overseas sales, will also accompany the Russian delegates.
The Russians will make visits across Korea to GC’s two factories, one located in Hwasun, 270km south of Seoul and another in Ochang, 100km southeast of Seoul, to examine whether the facilities are suitable for CoviVac production.
They will also have talks at the Korean government-funded Animal Cell Validation Support Center in Andong, 200km southeast of Seoul.
The Animal Cell Validation Support Center, founded in December 2020, is a contract manufacturing organization (CMO) for clinical vaccines. It helps domestic firms develop vaccine candidate substances and conduct global non-clinical and clinical tests.
COVID-19 Vaccines Produced in Korea through Contract Manufacturing
| Korean Manufacturer | Vaccine Developer | Contract Date |
| Green Cross | Russia (CoviVac) |
Mar 2021 (factory visit) |
| Binex | Russia (Sputnik V) |
Apr 2021 |
| Isu Abxis | Apr 2021 | |
| Hankook Korus Pharm | Apr 2021 | |
| SK Bioscience | Oxford-AstraZeneca | Jul 2020 |
| Novavax | Aug 2020 | |
| Green Cross | CEPI | Oct 2020 |
(source: each company)
Chumakov Center and CoviVac
Established during the Soviet era in 1957, the Chumakov Center is currently Russia’s largest vaccine developer. It supplies a range of vaccines to WHO and UNICEF, and is best known for its in-house developed polio vaccine widely distributed across multiple continents.
The center is currently conducting phase three clinical trials with CoviVac, after showing 95% efficacy in the second phase.
CoviVac uses the method of injecting an “inactivated”, or killed, virus to our body.
The inactivated method has less side effects compared to the “live-attenuated” method, which injects a living yet weakened virus for stronger and longer-lasting immune response.
The inactivated method has been widely used to develop vaccines for a range of other diseases including polio, rabies, influenza and hepatitis A.
DISCUSSION DETAILS
A successful deal will allow GC to export CoviVac vaccine to nine member countries of the CIS (Commonwealth of Independent States), adding hundreds of millions of dollars to GC’s annual revenues.
The CIS countries including Russia have already ordered around 300 million doses of CoviVac, of which the production of 100 million doses is currently in discussion with GC. South Korea’s Thelma Therapeutics will be in charge of distributing the vaccine to the CIS countries.
“The Russians wanted to produce more volume in South Korea, but GC can currently take around 100 million doses only, due to tight operation capacity of its manufacturing facilities”, said an industry source.
GC has reportedly offered the Russians both the production of undiluted vaccine solutions and the packaging of the finished products.
Hwasun factory will be in charge of the vaccine production, while Ochang factory will package the finished goods by filling the vaccine into the syringes. Ochang factory can annually produce up to 1 billion doses, assuming an 8-hour operation per day.
“GC’s operating margin will surpass 50% if it can land deals on both the solution part and the finished goods part,” commented an industry source.
The industry expects that GC, Thelma Therapeutics and the Russian officials will sign a technology transfer agreement and discuss pricing and scope of the deal during the visit in March, prior to the main contract likely to take place in mid-April.
Write to Woo-Sub Kim at duter@hankyung.com
Daniel Cho edited this article.
-
 Business & PoliticsTrump Jr. meets Korean business chiefs in back-to-back sessions
Business & PoliticsTrump Jr. meets Korean business chiefs in back-to-back sessionsApr 30, 2025 (Gmt+09:00)
-
 Korean chipmakersSamsung in talks to supply customized HBM4 to Nvidia, Broadcom, Google
Korean chipmakersSamsung in talks to supply customized HBM4 to Nvidia, Broadcom, GoogleApr 30, 2025 (Gmt+09:00)
-
 EnergyLS Cable breaks ground on $681 mn underwater cable plant in Chesapeake
EnergyLS Cable breaks ground on $681 mn underwater cable plant in ChesapeakeApr 29, 2025 (Gmt+09:00)
-
 Business & PoliticsUS tariffs add risk premium to dollar assets: Maurice Obstfeld
Business & PoliticsUS tariffs add risk premium to dollar assets: Maurice ObstfeldApr 29, 2025 (Gmt+09:00)
-



