Batteries
POSCO Future M to import natural graphite from Africa
Korea's sole anode producer has signed a deal with Australia’s Syrah Resources to import up to 60,000 tons of graphite per year
By Mar 01, 2024 (Gmt+09:00)
3
Min read
Most Read
LG Chem to sell water filter business to Glenwood PE for $692 million


KT&G eyes overseas M&A after rejecting activist fund's offer


Kyobo Life poised to buy Japan’s SBI Group-owned savings bank


StockX in merger talks with Naver’s online reseller Kream


Meritz backs half of ex-manager’s $210 mn hedge fund
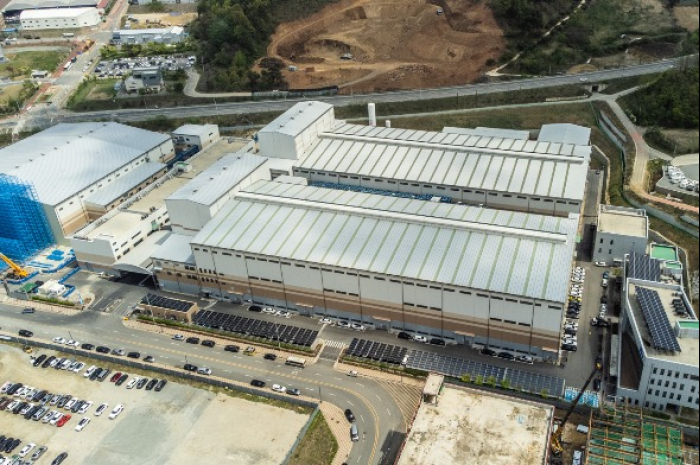



South Korea’s only anode materials producer POSCO Future M Co. will import a maximum 60,000 tons of natural graphite products from Balama Graphite Operations in Mozambique operated by Australia’s Syrah Resources Ltd. every year for six years.
The Australian mining company reported the long-term deal with the Korean battery materials company in Australian Securities Exchange’s regulatory filing on Friday.
The graphite supply deal is expected to help POSCO Future M reduce its nearly 100% reliance on natural graphite imports from China, a move expected to accelerate the diversification of its graphite suppliers as part of its efforts to qualify for tax incentives under the US Inflation Reduction Act (IRA).
The IRA requires that at least half the value of critical minerals and materials in EV batteries must be sourced from North America or its free trade partners.
On the day of the groundbreaking ceremony of its fifth cathode materials plant for nickel, cobalt and aluminum (NCA) batteries about a week ago, POSCO Future M’s Chief Executive Kim Jun-Hyung unveiled the company’s plan to import natural graphite from Africa, including Madagascar, to meet the IRA requirements.
Investing in a graphite mine in the continent was considered another option, he said.

SIX-YEAR DEAL FROM 2025 AT THE EARLIEST
Under the six-year deal, POSCO Future M will import up to 2 kilotons (kt) of natural graphite per month in the year following commissioning. This can be increased to 5 kt per month, with at least six months’ notice, from the second year of the deal to the end of the term.
The Korean company agreed to notify Syrah of the commencement date of the graphite import on or before Dec. 31, 2025.
The two parties also agreed to mutually negotiate the price for the natural graphite quarterly over the term of the deal, according to Syrah.
The maximum annual imports of natural graphite products from Balama, Syrah’s mine in Mozambique, will reach 60,000 tons, enough to produce 30,000 tons of natural graphite anode materials.
This accounts for about 40% of POSCO Future M’s yearly natural graphite anode materials production capacity of 74,000 tons.
SUPPLIER DIVERSIFICATION
Considering that POSCO Future M and its Korean peers are greatly exposed to geopolitical risks such as the ongoing US-China political and trade wars, natural resource supplier diversification is a key to Korean battery and battery materials makers’ risk management.
To benefit from the IRA’s electric vehicle tax breaks starting in 2025, EV batteries must not be made with any critical minerals supplied by the so-called foreign entity of concern (FEOC), which is highly likely to include companies in China.
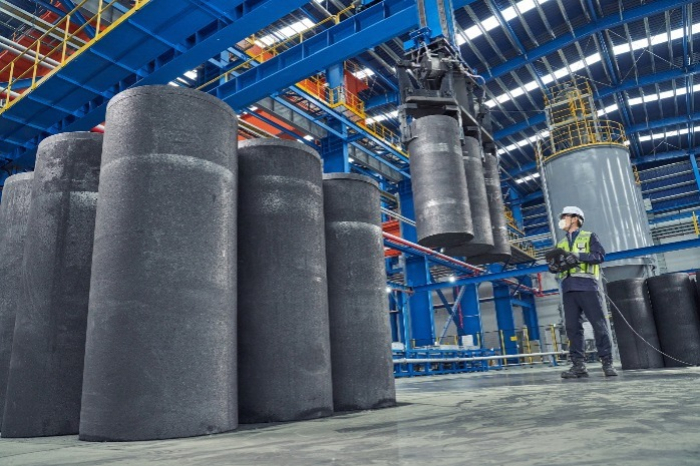

In an apparent response to the US discriminative move, China in October last year announced a new rule to limit exports of the country’s high-purity, high-hardness and high-intensity synthetic graphite, as well as natural flake graphite and its byproducts for a security reason.
Despite the new rule, which took effect in December last year, Beijing has issued spherical graphite product exports by Chinese companies to POSCO Future M without a single rejection.
But concerns remain that Beijing could scapegoat Korean battery and battery materials makers by putting a sudden complete ban on core battery mineral exports, according to industry observers.
In 2022, South Korea imported both synthetic and natural graphite products for battery anode materials worth $241 million, of which 93.7% were shipped from China, according to data from Korea’s Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy.
China controls more than 80% of global graphite supply.
This is why POSCO Future M has decided to import graphite flakes for a plan to build a graphite processing plant to produce spherical graphite, also known as battery-grade graphite that is consumed as an anode in lithium-ion batteries.
Flake graphite concentrate is processed into ultra-high-purity with particle sizes and then these are used as a battery anode material.
According to industry sources, POSCO Future M is expected to announce a plan soon to add facilities to process flake graphite into spherical graphite.
The company unveiled a plan in its investor relations document in January to venture into self-producing spherical graphite products.
Write to Hyung-Kyu Kim at khk@hankyung.com
Sookyung Seo edited this article.
More to Read
-
 BatteriesPOSCO to build world's largest battery cathode plant cluster
BatteriesPOSCO to build world's largest battery cathode plant clusterFeb 22, 2024 (Gmt+09:00)
2 Min read -
 BatteriesPOSCO Future M to sharply raise synthetic graphite output
BatteriesPOSCO Future M to sharply raise synthetic graphite outputJan 17, 2024 (Gmt+09:00)
2 Min read -
 BatteriesChina’s graphite export curbs deal blow to Korean battery sector
BatteriesChina’s graphite export curbs deal blow to Korean battery sectorOct 20, 2023 (Gmt+09:00)
3 Min read -
 BatteriesS.Korea's Posco International secures graphite in Africa
BatteriesS.Korea's Posco International secures graphite in AfricaSep 04, 2023 (Gmt+09:00)
1 Min read -
Comment 0
LOG IN


